Search engine optimisation (SEO) has seen significant changes from the early days of keyword stuffing. With the introduction of search generative experience,, which uses artificial intelligence (AI) to present search results conversationally, understanding user intent has become a critical component of modern SEO strategies.
Over the years, we have seen a shift from the traditional keyword-based search to a semantic search that better understands the context and intent behind a user’s search query. By distinguishing whether a user is seeking information, looking to make a purchase or finding a specific website, you can tailor your content strategies to meet the precise needs of your audience.
This alignment not only enhances the user experience (UX) but also boosts the relevance of search results, ultimately helping you to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). Let’s take a look at what semantic search is and how you can ensure that your site is optimised for it.
Semantic search has been developed to help search engines better understand and match queries to a searcher’s intent in the SERPs. This enables search engines to deliver more accurate and relevant results by understanding and interpreting the user’s needs and expectations.
This search engine evolution marks a significant advancement from the initial keyword-focused algorithms. In the early stages, search engines relied heavily on the presence of exact-match keywords within web content to rank pages. However, this method often fails to satisfy the user’s information-seeking needs, leading to irrelevant or low-quality search results.
The incorporation of machine learning and AI has been pivotal in the transformation of search results. These technologies allow search engines to analyse vast amounts of data, learn from user interactions and continually improve their understanding of search queries’ context and intent.
An example of how Google has integrated AI into its search engine
Google’s introduction of the RankBrain algorithm uses machine learning to interpret queries and measure how users interact with the results.
An example of how Bing has integrated AI into its search engine
Bing utilises AI through its Microsoft Cognitive Services to better understand the context of a query, delivering results that are more personalised and relevant to the user’s intent.
These advancements have created a more intuitive search experience, creating a seamless bridge between human queries and the digital information available online.
Optimising your site for semantic search offers several benefits that are crucial in enhancing your visibility and engagement online. Here are some of the key benefits of optimising for semantic search:
Improved Search Engine Rankings: By aligning content with the context and intent of search queries, your site is more likely to be viewed favourably by search engines.
Enhanced UX: Optimising for semantic search ensures that users find the content that matches their search intent more accurately, improving satisfaction and engagement with your website.
Increased Organic Traffic: With better rankings and a more positive UX, you can attract more organic traffic, reducing the reliance on paid channels.
Greater Content Relevance: By focusing on topics, entities and user intent, content becomes more relevant and useful to the audience, establishing your website as a credible authority in the field.
Competitive Edge: In a competitive digital landscape, the ability to effectively leverage semantic search can provide a crucial competitive advantage by connecting with users more effectively than competitors.
Accessibility & Inclusion: By making content more understandable and easier to find for both search engines and users, optimising for semantic search promotes inclusivity.
To fully understand how semantic search works, we first need to define the meaning behind the fundamental element of semantic search: Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP is a field of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language.
The ultimate objective of NLP is to read, decipher and make sense of human language. It involves a range of technologies for analysing and interpreting human language, covering both written and spoken language. This can include tasks such as language translation, sentiment analysis and speech recognition.
NLP is crucial for semantic search as it enables search engines to process and understand natural language queries, facilitating a more accurate interpretation of user intent and the context of search queries.
Semantic search leverages NLP to understand the context, intent and meanings within a user’s query. This approach allows for a better search experience, providing results that are tailored not just to the specific words, but to the intended meaning behind those words.
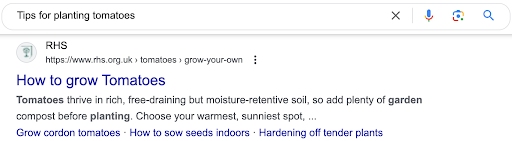
Example 1: “Tips for planting tomatoes”
Traditional keyword-based search engines might focus on returning pages that contain the exact match keywords in the query. However, a semantic search understands that the user is likely seeking advice on how to grow tomatoes. Semantic searches for this term will likely return results like the best practices for planting tomatoes and guides on tomato cultivation.
Example 2: “Jaguar”
Semantic search is also understanding queries that have multiple meanings depending on context. In a keyword-based search system, results might indiscriminately include references to the animal or the car brand. Semantic search would determine the most likely context of the search based on tailored cues such as recent search history to deliver results more accurately aligned with the user’s intent.

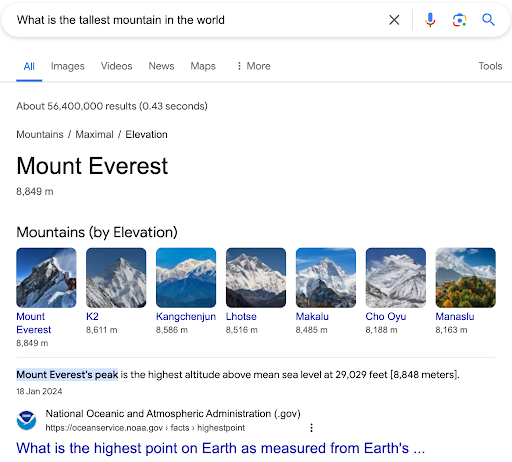
Example 3: “What is the tallest mountain in the world?”
Through NLP and machine learning, search engines are capable of understanding complex queries and can provide answers directly. When asking what the tallest mountain in the world is, semantic search will include a highlighted snippet directly answering the question with “Mount Everest”.
Search intent, also known as user intent, is the underlying reason that prompts a user to perform a search. Search intent can be categorised into four main types:
Informational: The user is seeking information. This can include queries like “how to bake a cake”.
Navigational: The user wants to visit a specific website or page. This can include queries like “Facebook login”.
Transactional: The user intends to complete a transaction or purchase. This can include queries like “best deals on dog food”.
Commercial: The user is considering making a purchase and wants to compare options or get more information before making a decision. This can include queries like “What is the best TV”.
Aligning content with user intent is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that the content meets the needs and expectations of the reader, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement. When users find the answers they’re looking for through your content, they’re more likely to trust your website and return in the future.
Additionally, search engines aim to provide the most relevant, helpful results to users by using algorithms that evaluate how well your content matches the intent of the query. By designing content that closely aligns with the search intent, you can improve your chances of ranking higher on search engine results pages (SERPs).
Selecting keywords with strong user intent is imperative for the success of any content strategy. At Proof3, we have access to a variety of helpful tools and resources to identify relevant keywords, as well as question-based keywords relating to the term. Here are some criteria that we consider when selecting keywords with a strong user intent:
Relevance: The keywords should be highly relevant to what you’re offering.
Search Volume: Keywords have a good search volume, whilst still being highly relevant to the page.
Competition: We will assess the level of competition for each keyword. It can sometimes be more strategic to target less competitive keywords with a slightly lower search volume to achieve higher rankings.
Keyword Intent: Keywords match the intended user intent as closely as possible.
By using a range of criteria and tools, we can help you to identify keywords that more accurately align your content with the user intent, helping your content to get higher visibility and engagement in the semantic search landscape.
Structured data markup is a way to annotate content on your website, making it understandable for search engines. With the help of schema.org, you can communicate directly with search engines about the contents meaning, context and relationship between entities.
Implementing schema markup on your website involves selecting the most appropriate schema types (article, event, product) for your content, and then using HTML tags to highlight properties and attributes of the content according to the schema.org vocabulary.
If you’d like help with structured data on your site, get in touch. Our SEO team can conduct a thorough structured data audit to ensure that your site is getting the most out of schema markup.
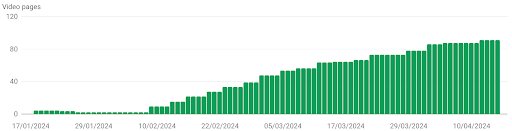
Below is the result of how we helped one of our clients to ensure that their video pages are indexed. As part of our structured data audit, we provided the client with a tailored video structured data template and a step-by-step guide on how to correctly implement the markup. By providing our client with everything they needed to ensure that their video structured data was implemented correctly, they went from 2 indexed video pages before our recommendations, to 91 indexed video pages.
Important elements that we suggested in our video structured data audit included:
Use video thumbnails
Ensure that the video is prominently displayed at the top of the page
Ensure that basic structured data information is implemented in the code
Add Video XML sitemap
By properly implementing structured data, your website can achieve greater visibility and engagement in search results, making it an essential component of modern SEO and semantic search strategies.
Rich snippets can be added to your existing HTML to allow search engines to better understand the information contained on your web pages. These snippets then enable search engines to display more informative results to users, often including additional data such as star ratings, author photos, price ranges and preparation times for recipes.
By providing a more comprehensive overview of what your page entails, rich snippets can significantly improve UX, leading to higher engagement rates.

Knowledge graphs use a network of interconnected entities (people, places, things) and their attributes to store and process information in a way that mirrors human understanding. They play a pivotal role in SEO and semantic search because they enable search engines to interpret and present information in a more intuitive, human-like manner. By understanding the relationships and context between these entities, search engines can provide richer, more accurate search results.
To ensure your content is reflected in relevant knowledge graphs, we recommend that you follow these strategies:
Structured Data Markup: Ensure that structured data is available and marked up correctly using schema.org.
Consistent Entity Use: Regularly refer to entities (names, places, products, etc.) consistently across your content.
Build Topic Clusters: Create content clusters around specific topics. This allows you to interlink pages or posts, signalling to search engines your authority on this topic and improving the chances of being included in related knowledge graphs.
External Validation: External links from reputable sites and mentions of your content across the web can help contribute to the credibility and authority of your site.
Driven by the growing trend of voice-activated assistants like Siri, Alexa and Google Assistant, voice search optimisation is becoming increasingly important. This shift towards voice search changes how users interact with search engines. These queries tend to be more conversational, longer and often phrased as complete sentences or questions.
This shift in user behaviour is pivotal in semantic SEO, as search engines have adapted to better understand and process natural language queries more effectively to deliver accurate results.
To optimise content for voice search, follow these best practices:
Focus on Natural Language & Question-Based Keywords
Create FAQ pages/section
Ensure Mobile-Friendliness
Use Structured Data Markup
Improve Local SEO
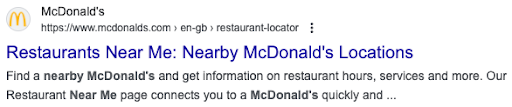
In the rapidly evolving landscape of semantic search, high-quality, relevant content is becoming increasingly important. The shift in how search engines operate means that content not only needs to incorporate the right keywords but also addresses the user’s intent in a meaningful and comprehensive manner.
To excel in this semantic search environment, it’s important to create content that satisfies both users and search engines. Here are some tips to achieve this:
Understand User Intent: We can help you to identify the questions and needs of your target audience.
Write For Your Audience: Your primary focus should be on providing value to your audience. Create content that is engaging, informative and addresses the needs or problems of your readers.
Use Keyword Variations: Incorporate synonyms and related terms that people might use to search for your content. An example of a site that does this well is Nike, by uses both “sneakers” and “trainers” throughout their content.
Effectively Structure Your Content.
Keep Content Fresh & Up-To-Date: Regularly updating your content ensures it remains relevant and useful.
Leverage Multimedia & Interactive Elements.
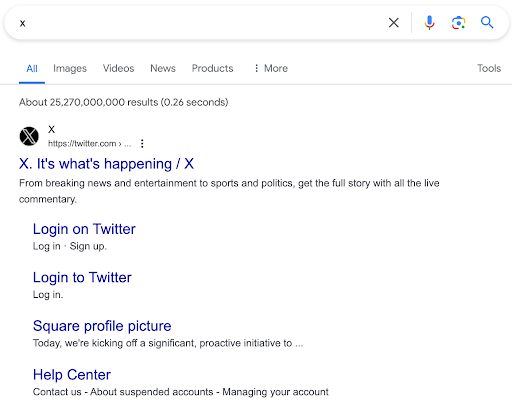
X (formally Twitter) is a fantastic example of how search engines interpret the intent of a user’s search. When searching for X, search engines understand that users intend to log in or sign up for
X, as shown below.
Ultimately, by focusing on high-quality, relevant content that satisfies both users and search engines, you can enhance your semantic search optimisation strategies.
Evaluating the success of semantic SEO strategies requires a focus on specific key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect both the visibility and effectiveness of your content within a semantic search context. These KPIs include:
Organic Traffic
Positioning
CTR
Bounce Rate
At Proof3, we have access to a range of various tools and platforms to track and analyse these KPIs effectively. This way, we can accurately measure the impact of your semantic SEO efforts, making informed decisions to continuously improve the effectiveness and visibility of your content.
In this article, we’ve discussed the significance of creating content that resonates with your audience, optimising for mobile devices and the benefits of incorporating user intent and semantic search best practices into your SEO strategy.
If you need guidance on implementing user intent and semantic search strategies effectively, don’t hesitate to get in touch. Our team is here to help you unlock the full potential of your SEO efforts to drive meaningful results.
Start optimising with the future of search in mind and watch your digital presence transform
